
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples are widely used in spatial transcriptomics, especially in clinical settings where long-term tissue preservation is essential. For studies using the 10x Genomics Visium HD platform, high-quality FFPE samples are crucial for successful downstream spatial gene expression analysis. This article outlines key technical considerations during FFPE preparation, from fixation to embedding, to help researchers avoid common pitfalls.
Tip 1: During tissue excision, handle the sample gently to prevent mechanical damage that may compromise fixation quality. External pressure can lead to:
Ischemia
Coagulative necrosis from electrocautery
Hemorrhage due to surgical trauma
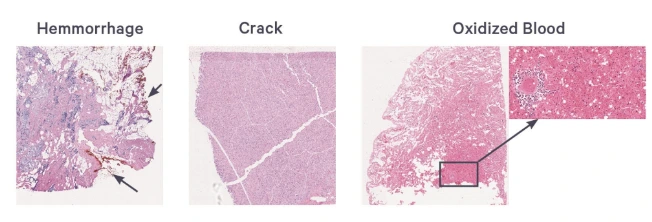
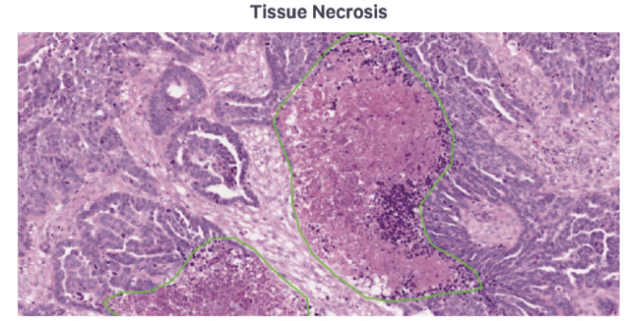
Tip 2: Fix the tissue as soon as possible after excision. If immediate fixation is not feasible (e.g., due to prolonged bleeding or post-mortem delay), store the sample in an isotonic solution temporarily. Ideally, fixation should begin within 4 hours of tissue removal to avoid autolysis and RNA degradation.
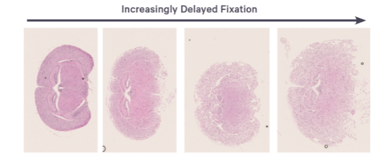
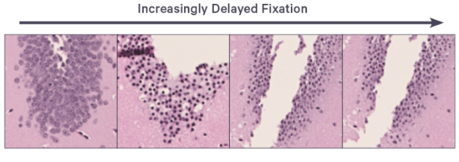
Using 10% neutral-buffered formalin or 4% paraformaldehyde is standard practice. However, both under-fixation and over-fixation can negatively impact spatial transcriptomic performance.
Residual enzymatic activity leading to degradation of proteins, RNA, and lipids
Morphological artifacts such as chromatin distortion or excessive cytoplasmic eosin staining
Autolysis and tissue separation artifacts
Excessive crosslinking, lipid oxidation, or loss of antigenicity
Tissue hardening, making sectioning difficult
Morphological distortions including cell shrinkage or nuclear overstaining
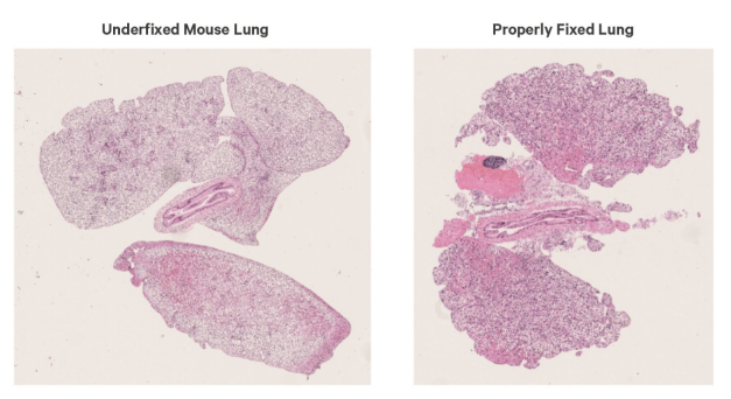
Before fixation, consider the species, tissue type, and disease model. During fixation, ensure:
Proper reagent penetration
Time-controlled processing
Avoidance of prolonged storage in fixatives
Poor processing at this stage can directly affect RNA integrity and sectioning quality.
Gradually replace residual water in the tissue with ethanol through graded concentrations. Incomplete dehydration can compromise tissue structure and result in poor morphology.
Ethanol is removed using an organic solvent (e.g., xylene). Inadequate clearing can hinder wax infiltration, leading to brittle blocks that are hard to section.
After clearing, tissues are immersed in molten paraffin wax (60–62°C). Incomplete infiltration may cause cavities and air gaps in the block. After infiltration, allow the wax to cool to 20°C for embedding.
Tip: Use high-quality, low-melting paraffin and regularly monitor wax temperature to avoid overheating.
Embed the tissue in paraffin blocks while preserving anatomical orientation for accurate downstream sectioning.
Tip: Clearly document tissue orientation during embedding to ensure correct alignment during sectioning.
Refresh reagents regularly to avoid contamination or over-fixation.
Do not store samples in fixatives for extended periods.
Perform dehydration, clearing, infiltration, and embedding consecutively without long delays.
If immediate dehydration is not possible, transfer tissue to 70% ethanol for short-term storage.
Store paraffin blocks at 4°C in a dry environment to preserve integrity. Avoid heat and humidity.
Our technical team is here to help. Whether you're working with FFPE or fresh-frozen tissues, from human to plant samples, we offer comprehensive support across the entire workflow—including sample preparation, library construction, and bioinformatics analysis.
Our spatial transcriptomics and single-cell sequencing services are tailored to diverse research areas such as oncology, neuroscience, and developmental biology. Reach out to explore how we can support your project from start to finish.
**Credit: All figures presented in this article are credited to 10x Genomics unless otherwise noted.
Germany: Arnold-Graffi-Haus / D85 Robert-Rössle-Straße 10 13125 Berlin
United States: (CA) 2 Goddard, Irvine, CA 92618
United States: (IL) 8255 Lemont Rd, #1, Darien, IL 60561
Hong Kong: Room 618, Building 6, Hong Kong Science Park, Pak Shek Kok, Hong Kong
Germany: Arnold-Graffi-Haus / D85 Robert-Rössle-Straße 10 13125 Berlin
United States: (CA) 2 Goddard, Irvine, CA 92618
United States: (IL) 8255 Lemont Rd, #1, Darien, IL 60561
Hong Kong: Room 618, Building 6, Hong Kong Science Park, Pak Shek Kok, Hong Kong